-
冬天工業(yè)超聲波清洗機(jī)的保養(yǎng)要注意什么?
-
可過(guò)濾循環(huán)的超聲波清洗設(shè)備介紹
-
中小型超聲波清洗機(jī)有什么使用共性嗎?
-
超聲波清洗機(jī)為什么不要用強(qiáng)酸強(qiáng)堿?
-
全自動(dòng)超聲波清洗機(jī)在汽車(chē)制造業(yè)的應(yīng)用范圍
-
恒溫超聲波清洗機(jī)的特點(diǎn)有哪些?
-
超聲波清洗適宜頻率有哪些?
-
低溫廢水回收設(shè)備的使用
-
多槽手動(dòng)超聲波清洗機(jī)的使用
-
標(biāo)準(zhǔn)超聲波清洗機(jī)與非標(biāo)準(zhǔn)超聲波清洗機(jī)的區(qū)別
 服務(wù)熱線電話
服務(wù)熱線電話
400-6188-756
碳?xì)淝逑礄C(jī)清洗流程詳解:多步驟協(xié)作的高效清潔之道
來(lái)源:http://www.xgsic.com/ 時(shí)間: 2025-07-21 瀏覽次數(shù): 0
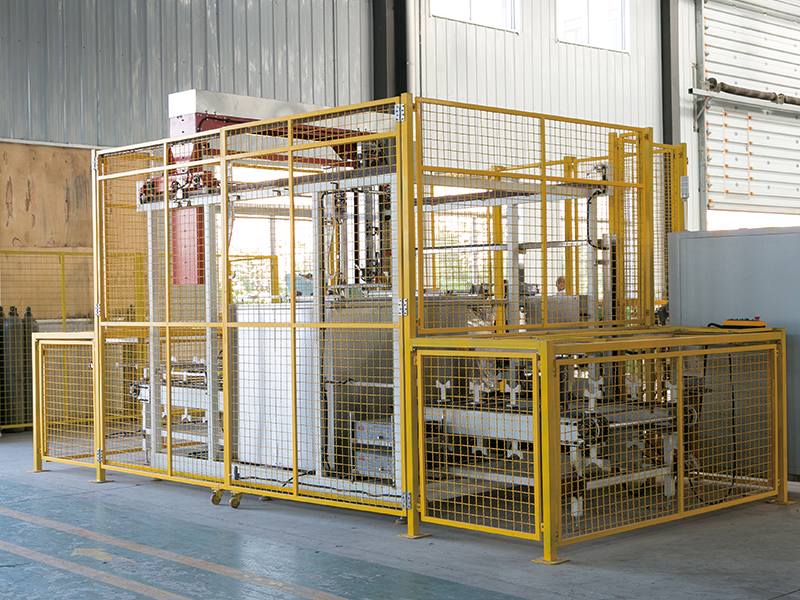
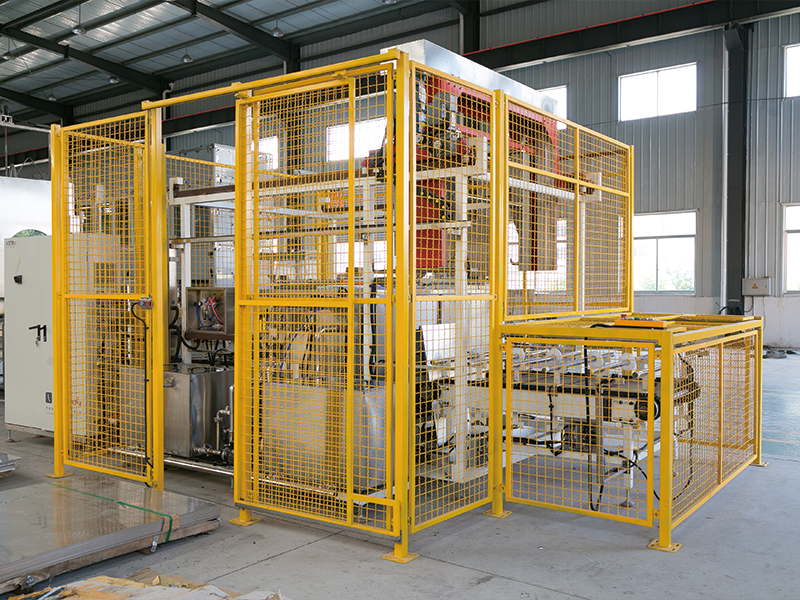
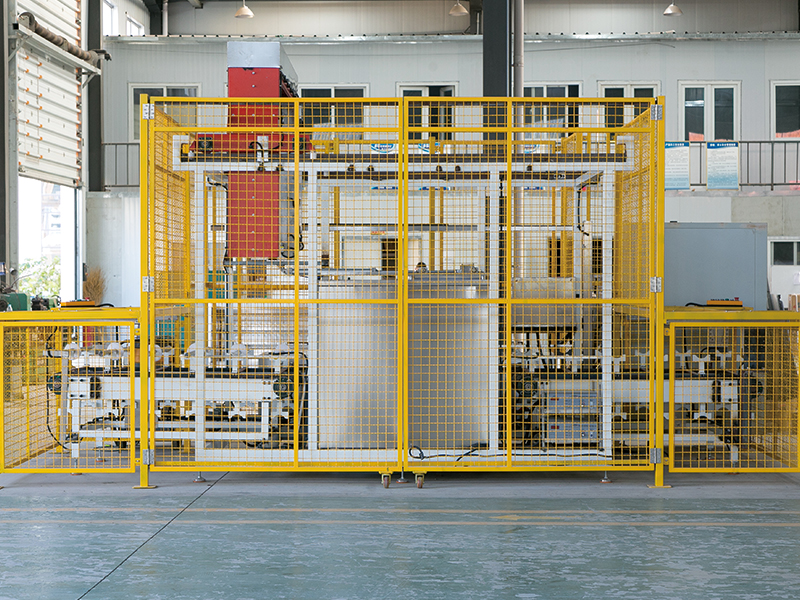
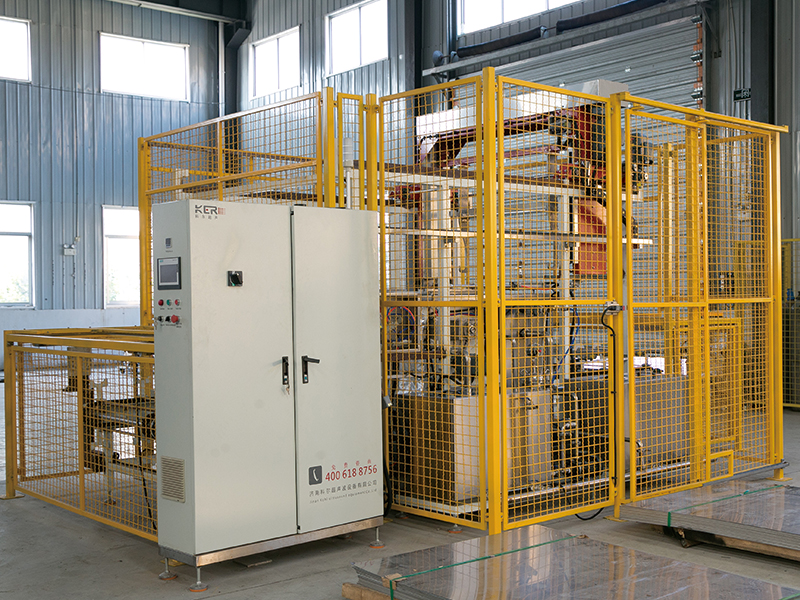
碳?xì)淝逑礄C(jī)作為工業(yè)清洗領(lǐng)域的高效設(shè)備,其清洗流程經(jīng)過(guò)精心設(shè)計(jì),能夠確保工件得到徹底清潔,同時(shí)實(shí)現(xiàn)碳?xì)淙軇┑难h(huán)利用。了解這一流程,有助于更好地理解其工作原理和高效性的來(lái)源。
As an efficient equipment in the industrial cleaning field, the hydrocarbon cleaning machine has a carefully designed cleaning process that ensures thorough cleaning of the workpiece while achieving the recycling of hydrocarbon solvents. Understanding this process helps to better understand its working principle and the sources of efficiency.
清洗流程的第一步是工件預(yù)處理。在將工件放入清洗機(jī)之前,需要對(duì)其進(jìn)行簡(jiǎn)單處理。操作人員會(huì)先清除工件表面附著的大塊雜質(zhì),如金屬碎屑、灰塵結(jié)塊等,避免這些雜質(zhì)進(jìn)入清洗系統(tǒng)后污染溶劑或堵塞設(shè)備管路。對(duì)于帶有復(fù)雜結(jié)構(gòu)的工件,比如帶有深孔、縫隙的零件,會(huì)檢查是否有纏繞的絲線、殘留的大塊油污等,必要時(shí)進(jìn)行手工初步清理,為后續(xù)的深度清洗做好準(zhǔn)備。預(yù)處理雖簡(jiǎn)單,卻能有效提高整體清洗效率,減少設(shè)備運(yùn)行中的故障風(fēng)險(xiǎn)。
The first step in the cleaning process is workpiece pretreatment. Before placing the workpiece into the cleaning machine, it needs to be subjected to simple processing. The operator will first remove large impurities attached to the surface of the workpiece, such as metal debris, dust clumps, etc., to avoid these impurities entering the cleaning system and contaminating the solvent or blocking the equipment pipeline. For workpieces with complex structures, such as those with deep holes and gaps, they will be checked for tangled threads, residual large oil stains, etc. If necessary, manual preliminary cleaning will be carried out to prepare for subsequent deep cleaning. Although preprocessing is simple, it can effectively improve overall cleaning efficiency and reduce the risk of equipment failure during operation.
接下來(lái)進(jìn)入核心的清洗階段,這一階段通常包含多個(gè)步驟,且會(huì)根據(jù)工件的污染程度和清潔要求進(jìn)行調(diào)整。首先是浸泡清洗,將預(yù)處理后的工件放入裝有碳?xì)淙軇┑那逑床壑校屓軇┏浞职ぜL細(xì)淙軇?huì)逐漸滲透到油污內(nèi)部,對(duì)其進(jìn)行溶解,對(duì)于一些附著不牢固的油污,在浸泡過(guò)程中就會(huì)脫離工件表面。浸泡時(shí)間根據(jù)工件油污的厚度和性質(zhì)而定,一般從幾分鐘到幾十分鐘不等。
Next, we enter the core cleaning stage, which usually involves multiple steps and will be adjusted according to the degree of contamination and cleaning requirements of the workpiece. Firstly, soak and clean the pre treated workpiece by placing it into a cleaning tank filled with hydrocarbon solvents, allowing the solvent to fully envelop the workpiece. Carbon hydrogen solvents will gradually penetrate into the oil stains and dissolve them. For some oil stains that are not firmly attached, they will detach from the surface of the workpiece during the soaking process. The soaking time depends on the thickness and nature of the oil stains on the workpiece, generally ranging from a few minutes to several tens of minutes.

浸泡之后往往會(huì)進(jìn)行超聲波清洗,這一步是提高清洗效果的關(guān)鍵。清洗槽內(nèi)的超聲波發(fā)生器產(chǎn)生高頻振動(dòng),使碳?xì)淙軇┲行纬蔁o(wú)數(shù)微小的氣泡。這些氣泡在振動(dòng)過(guò)程中不斷生成、長(zhǎng)大,然后迅速破裂,產(chǎn)生強(qiáng)烈的沖擊力。這種沖擊力能夠作用于工件表面及縫隙、盲孔等難以清潔的部位,將浸泡后松動(dòng)的油污徹底剝離,確保工件每個(gè)角落都能得到清潔。超聲波清洗的頻率和功率會(huì)根據(jù)工件材質(zhì)和結(jié)構(gòu)進(jìn)行調(diào)節(jié),避免對(duì)精密零件造成損傷。
After soaking, ultrasonic cleaning is often performed, which is the key to improving the cleaning effect. The ultrasonic generator in the cleaning tank generates high-frequency vibration, causing countless tiny bubbles to form in the hydrocarbon solvent. These bubbles continuously generate and grow during the vibration process, and then quickly burst, generating strong impact force. This impact force can act on the surface of the workpiece, as well as on difficult to clean areas such as gaps and blind holes, thoroughly removing any loose oil stains after soaking, ensuring that every corner of the workpiece can be cleaned. The frequency and power of ultrasonic cleaning will be adjusted according to the material and structure of the workpiece to avoid damage to precision parts.
清洗完成后,工件會(huì)進(jìn)入漂洗階段。經(jīng)過(guò)前面的清洗,工件表面可能還殘留少量的溶劑和未完全脫離的細(xì)小污染物,漂洗就是為了去除這些殘留物。漂洗槽中通常裝有經(jīng)過(guò)蒸餾提純的純凈碳?xì)淙軇ぜ谄渲性俅谓莼蚴艿絿娏埽酶蓛舻娜軇⒈砻鏆埩舻碾s質(zhì)帶走,進(jìn)一步提高工件的潔凈度。對(duì)于要求極高的精密工件,可能會(huì)進(jìn)行多次漂洗,以確保達(dá)到規(guī)定的清潔標(biāo)準(zhǔn)。
After cleaning, the workpiece will enter the rinsing stage. After the previous cleaning, there may still be a small amount of solvent and incomplete detachment of small pollutants on the surface of the workpiece. Rinsing is to remove these residues. The rinsing tank usually contains pure hydrocarbon solvents that have been distilled and purified. The workpiece is soaked or sprayed in it again, and the residual impurities on the surface are taken away by the clean solvent, further improving the cleanliness of the workpiece. For precision workpieces with extremely high requirements, multiple rinses may be performed to ensure compliance with the specified cleaning standards.
漂洗之后是干燥處理。由于碳?xì)淙軇┚哂休^強(qiáng)的揮發(fā)性,干燥過(guò)程相對(duì)簡(jiǎn)便。工件被轉(zhuǎn)移到干燥槽后,設(shè)備會(huì)對(duì)其進(jìn)行加熱或通入熱風(fēng),加速溶劑的揮發(fā)。同時(shí),干燥槽通常與溶劑回收系統(tǒng)相連,揮發(fā)的溶劑蒸汽會(huì)被收集起來(lái),送入蒸餾裝置進(jìn)行處理,避免直接排放造成浪費(fèi)和污染。干燥時(shí)間根據(jù)工件的大小、材質(zhì)以及環(huán)境溫度而定,確保工件表面完全干燥,沒(méi)有溶劑殘留,不影響后續(xù)的加工或裝配工序。
After rinsing, it is dried. Due to the strong volatility of hydrocarbon solvents, the drying process is relatively simple. After the workpiece is transferred to the drying tank, the equipment will heat it or introduce hot air to accelerate the evaporation of the solvent. At the same time, the drying tank is usually connected to the solvent recovery system, and the evaporated solvent vapor is collected and sent to the distillation unit for treatment, avoiding direct discharge that may cause waste and pollution. The drying time depends on the size, material, and ambient temperature of the workpiece, ensuring that the surface of the workpiece is completely dry, without solvent residue, and does not affect subsequent processing or assembly processes.
最后是溶劑回收與凈化。在整個(gè)清洗過(guò)程中,使用過(guò)的碳?xì)淙軇?huì)被收集到蒸餾槽中,通過(guò)加熱使其蒸發(fā)成蒸汽。蒸汽進(jìn)入冷卻系統(tǒng)后液化,變成純凈的溶劑,重新輸送到清洗槽或漂洗槽中循環(huán)使用。而蒸餾后留下的殘?jiān)饕菑墓ぜ蟿冸x的油污和雜質(zhì),會(huì)被定期清理。這一環(huán)節(jié)不僅提高了溶劑的利用率,降低了運(yùn)行成本,還減少了廢棄物的排放,體現(xiàn)了碳?xì)淝逑礄C(jī)的環(huán)保特性。
Finally, solvent recovery and purification. During the entire cleaning process, the used hydrocarbon solvents will be collected in the distillation tank and heated to evaporate into steam. After entering the cooling system, the steam liquefies and becomes a pure solvent, which is then transported back to the cleaning or rinsing tank for recycling. The residue left after distillation, mainly consisting of oil stains and impurities peeled off from the workpiece, will be cleaned regularly. This step not only improves the utilization rate of solvents and reduces operating costs, but also reduces waste emissions, reflecting the environmental characteristics of hydrocarbon cleaning machines.
本文由碳?xì)淝逑礄C(jī)友情奉獻(xiàn).更多有關(guān)的知識(shí)請(qǐng)點(diǎn)擊:http://www.xgsic.com我們將會(huì)對(duì)您提出的疑問(wèn)進(jìn)行詳細(xì)的解答,歡迎您登錄網(wǎng)站留言.
This article is a friendly contribution from a high-pressure deburring cleaning machine For more information, please click: http://www.xgsic.com We will provide detailed answers to your questions. You are welcome to log in to our website and leave a message
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
相關(guān)文章
-
全自動(dòng)化噴淋清洗機(jī):核心清洗環(huán)節(jié)解析 2025-07-28
-
碳?xì)淝逑礄C(jī)清洗流程詳解:多步驟協(xié)作的高效清潔之道 2025-07-21
-
帶你體驗(yàn)通過(guò)式噴淋清洗機(jī)清洗流程 2025-07-16
-
噴淋清洗機(jī)清洗流程解析 2025-07-14
-
高壓去毛清洗機(jī)去除毛刺的方法解析 2025-07-11
-
噴淋清洗機(jī)高壓噴嘴流道設(shè)計(jì)對(duì)沖擊力的影響 2025-07-10
-
通過(guò)式旋轉(zhuǎn)清洗機(jī):中小型零件清洗好幫手 2025-07-09
-
高壓去毛刺清洗機(jī):技術(shù)特性與應(yīng)用優(yōu)勢(shì)解析 2025-07-08
-
多槽手動(dòng)超聲波清洗機(jī)的清洗流程講解 2025-07-07
-
碳?xì)淝逑礄C(jī):脫脂戰(zhàn)場(chǎng)上的 “附著力守護(hù)者” 2025-07-04


 新聞中心
新聞中心




 行業(yè)新聞
行業(yè)新聞







 魯公網(wǎng)安備37011202000628號(hào)
魯公網(wǎng)安備37011202000628號(hào)